In recent years, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has undergone significant changes in its tax landscape, with the introduction of UAE Corporate Tax Registration regulations. For businesses operating in the UAE, understanding the intricacies of Corporate Tax Registration, and filing in Dubai UAE is crucial to ensure compliance and avoid penalties. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the essential steps and considerations for UAE for filing taxes in the UAE.
Understanding Corporate Tax in the UAE
Historically known for its tax-friendly environment, the UAE has introduced UAE Corporate Tax Registration regulations to diversify its revenue streams and align with international standards. While the UAE does not impose federal corporate income tax on most businesses, certain activities and entities are subject to taxation at the federal and emirate levels.
Key Considerations for Business Registration
Determining Taxable Presence: Businesses must assess their taxable presence in the UAE to determine if they are liable for UAE Corporate Tax Registration. Factors such as physical presence, economic activity, and residency status play a crucial role in this determination.
Choosing the Right Tax Structure: Selecting the appropriate tax structure is essential for optimizing tax efficiency and compliance. Businesses can operate as onshore entities subject to federal corporate tax or as entities in free zones with tax exemptions, depending on their business activities and objectives.
Applying for Tax Registration: Once the taxable presence is established, businesses must apply for tax registration with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA). The registration process involves submitting relevant documents, including legal entity documents, trade licenses, and financial statements.
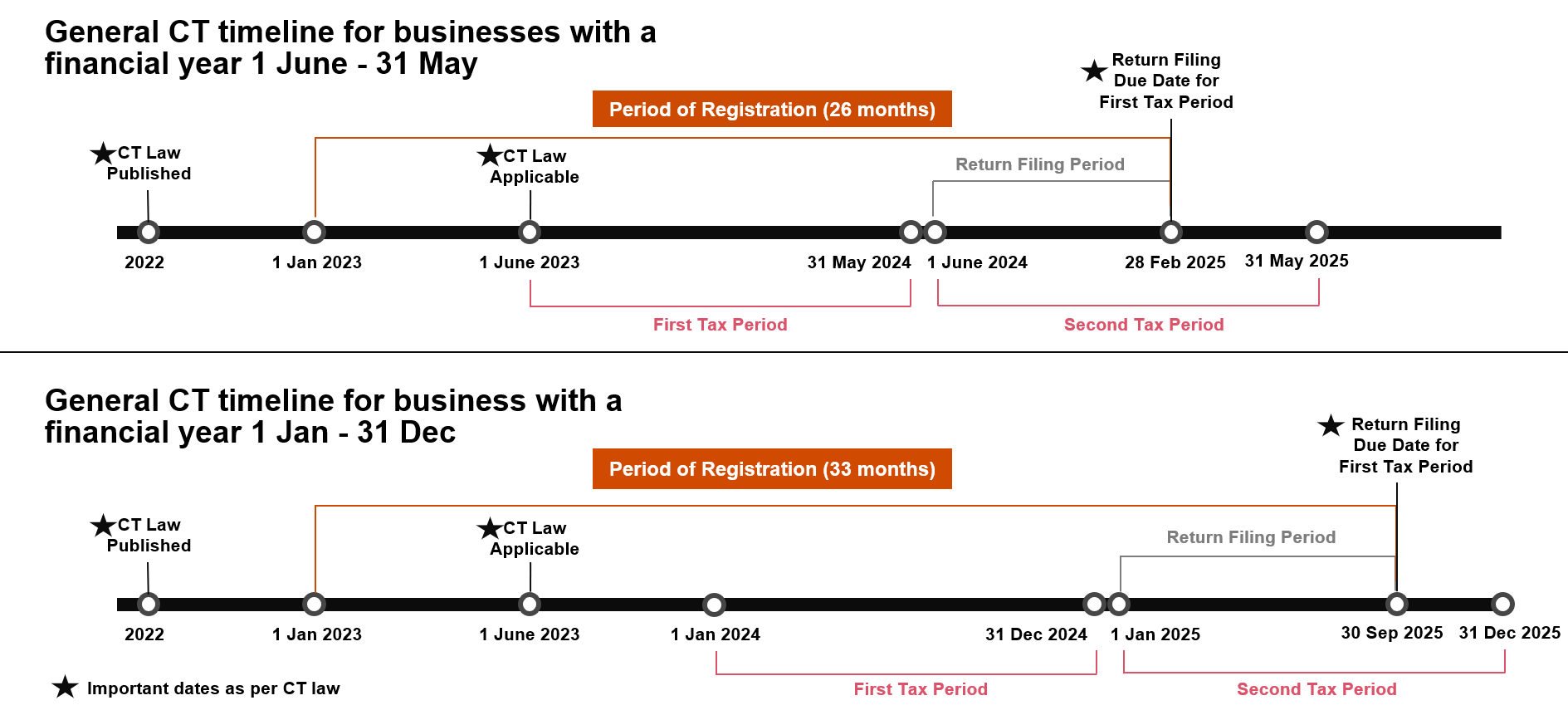
Illustrated below are examples of the registration, filing and payment deadlines associated for Taxable Persons with a Tax Period (Financial Year) ending on 31 May or 31 December (respectively).
Navigating the Filing Process
Maintaining Accurate Records: Effective tax compliance hinges on proper record-keeping practices. Businesses must maintain meticulous financial records to fulfill their tax obligations and streamline the filing process. This entails maintaining comprehensive records, including income statements, balance sheets, and transaction records. By keeping accurate and up-to-date financial documentation, businesses can ensure the accuracy of their tax calculations and facilitate smooth tax filings.
Preparing and Submitting Tax Returns: One of the core responsibilities of businesses subject to UAE Corporate Tax Registration is the preparation and submission of annual tax returns to the Federal Tax Authority (FTA). Tax returns serve as a comprehensive summary of a company’s financial activities throughout the fiscal year, detailing taxable income, deductions, and credits claimed. Properly completing and submitting tax returns in a timely manner is crucial to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and avoid potential penalties or fines.
Related: Key Points – UAE Corporate Tax
Compliance with Reporting Deadlines: Adherence to tax filing deadlines is paramount to maintaining compliance with UAE tax regulations. Businesses must stay vigilant and informed about the relevant reporting deadlines set by the FTA. Timely submission of tax returns and accompanying documentation is essential to meet regulatory requirements and avoid penalties. By proactively managing reporting deadlines and ensuring prompt submission of required tax filings, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to compliance and minimize the risk of regulatory sanctions.
Ensuring Compliance and Mitigating Risks
Seeking Professional Guidance: In navigating the complexities of UAE tax regulations, it’s crucial for businesses to enlist the expertise of tax advisors and consultants. These seasoned professionals offer invaluable insights into the intricacies of the tax landscape, helping businesses identify potential tax-saving opportunities and ensuring adherence to applicable laws. With their specialized knowledge, tax advisors can guide businesses through the nuances of tax compliance, offering tailored solutions to optimize their tax positions while minimizing risks.
Conducting Regular Audits and Reviews: Regular audits and reviews of tax compliance processes and procedures are essential components of effective tax governance. By systematically evaluating their tax compliance frameworks, businesses can proactively identify any areas of non-compliance or inefficiency. These audits provide valuable opportunities to assess the effectiveness of existing tax strategies and identify potential gaps or weaknesses in tax governance. Prompt implementation of corrective measures based on audit findings can bolster overall tax compliance, mitigate risks, and fortify the organization’s tax governance framework for sustained success.
Conclusion
Navigating the corporate tax landscape in the UAE demands a strategic approach and a keen awareness of regulatory intricacies. As businesses embark on the journey of Corporate Tax in Dubai UAE, they must prioritize meticulous planning, attention to detail, and compliance with relevant regulations. By adhering to the steps outlined in this comprehensive guide and leveraging professional expertise where necessary, businesses can navigate the complexities of the tax regime with confidence and efficiency.
The process of UAE Corporate Tax Registration entails more than just submitting paperwork; it requires a holistic understanding of tax laws, diligent record-keeping practices, and proactive compliance measures. Businesses must maintain accurate financial records, prepare, and submit tax returns in accordance with regulatory deadlines, and remain vigilant to evolving tax requirements. By embracing these responsibilities and staying abreast of regulatory updates, businesses can ensure their compliance with UAE tax laws and mitigate the risk of non-compliance penalties.